Mesopotamia social structure has been a subject of great interest to historians and archaeologists alike, as it provides insight into one of the world's earliest civilizations. This ancient region, situated between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, is often regarded as the cradle of civilization. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the social hierarchy, roles, and relationships that defined Mesopotamian society. Our exploration will highlight the various classes, occupations, and cultural aspects that shaped daily life in this fascinating era.
The social structure of Mesopotamia was complex and multifaceted, consisting of different classes that played specific roles within the community. Understanding this structure is crucial for those interested in ancient history, anthropology, and sociology. Through this article, we aim to provide an in-depth analysis of the social classes in Mesopotamia, including the ruling elite, priests, artisans, and farmers, among others.
As we journey through the layers of Mesopotamian society, we will also consider how this social structure influenced economic activities, governance, and cultural practices. By examining the interactions between these various social groups, we can gain a better understanding of how Mesopotamia laid the foundation for subsequent civilizations and their social systems.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Social Classes in Mesopotamia
- The Ruling Class
- The Priesthood
- Artisans and Merchants
- Farmers and Laborers
- Gender Roles in Mesopotamia
- Conclusion
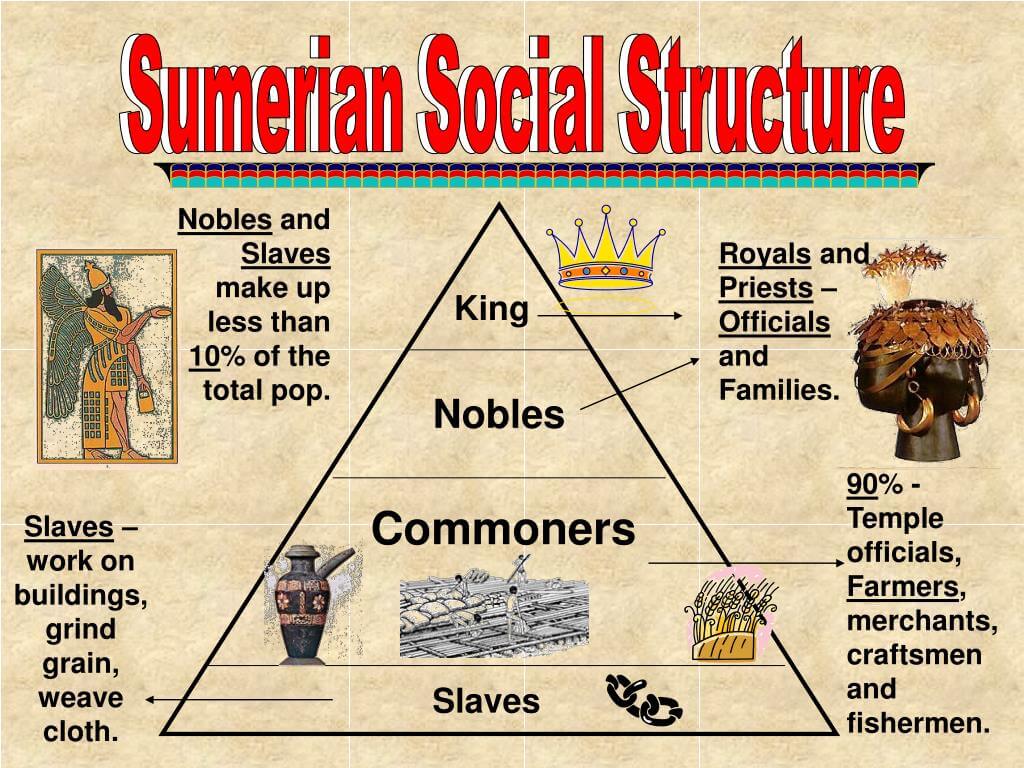
Social Classes in Mesopotamia
The social structure of Mesopotamia was characterized by a hierarchical system that consisted of several distinct classes. These classes included:
- The ruling class
- The priesthood
- Artisans and merchants
- Farmers and laborers
This hierarchy was not only a reflection of wealth and power but also determined the roles individuals played within society. The ruling class held significant political and economic power, while the lower classes were often involved in manual labor and agriculture.
The Ruling Class
The ruling class in Mesopotamia comprised kings, nobles, and high officials. They played a crucial role in governance and were responsible for making important decisions regarding laws, trade, and warfare. The rulers often claimed divine right, which legitimized their authority and reinforced their power among the populace.
Key characteristics of the ruling class included:
- Wealth accumulation through land ownership
- Control over military forces
- Influence in religious matters
Notable rulers, such as Hammurabi of Babylon, are remembered for their contributions to law and governance, further solidifying the importance of the ruling class in Mesopotamian society.
The Priesthood
The priesthood held a significant place in Mesopotamian social structure, acting as intermediaries between the gods and the people. They were responsible for conducting religious ceremonies, maintaining temples, and ensuring that the favor of the gods was secured for the community.
Key roles within the priesthood included:
- High priests: Leaders of religious practices and temple administration
- Temple workers: Individuals responsible for daily temple activities
- Diviners: Specialists in interpreting omens and signs from the gods
The wealth generated from temple resources contributed to the power of the priesthood, making them influential figures in both religious and political matters.
Artisans and Merchants
Artisans and merchants comprised the middle class in Mesopotamia. They played a vital role in the economy by producing goods and facilitating trade between different regions. Artisans were skilled in various crafts, including pottery, weaving, and metalworking, while merchants engaged in the exchange of goods both locally and internationally.
Characteristics of artisans and merchants included:
- Specialized skills that allowed for the production of high-quality goods
- Participation in trade networks that expanded economic opportunities
- Contribution to cultural exchange and the spread of ideas
Their economic activities were crucial for the prosperity of Mesopotamian cities, which thrived on trade and craftsmanship.
Farmers and Laborers
At the base of the social structure were farmers and laborers, who formed the majority of the population. They were essential for sustaining the agricultural economy of Mesopotamia, which relied on irrigation and farming practices to produce crops. Despite their critical role, they often faced harsh living conditions and limited social mobility.
Key aspects of farmers and laborers' lives included:
- Working long hours in the fields to cultivate crops
- Paying taxes to the ruling class and the priesthood
- Limited access to education and political power
Despite their lower social status, farmers and laborers were the backbone of Mesopotamian society and contributed significantly to its stability and growth.
Gender Roles in Mesopotamia
Gender roles in Mesopotamian society were defined by cultural norms and expectations. While men predominantly held positions of power and authority, women also played important roles within their families and communities.
Key points regarding gender roles included:
- Men were typically involved in public life, including politics and trade.
- Women were responsible for managing households and raising children.
- Some women, particularly in the upper classes, could hold property and engage in business activities.
The complexity of gender roles adds another layer of understanding to the social structure of Mesopotamia, highlighting the contributions of both men and women to society.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the social structure of Mesopotamia was characterized by a hierarchical system that shaped the lives of its inhabitants. The ruling class, priesthood, artisans, merchants, farmers, and laborers all played distinct yet interconnected roles within society. Understanding this social structure not only provides insight into the daily lives of Mesopotamians but also highlights the factors that contributed to the longevity and influence of this remarkable civilization.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on the Mesopotamia social structure in the comments below and explore more articles on ancient civilizations to deepen your understanding of history.
Thank you for reading! We hope to see you back here for more engaging content on ancient history and cultural studies.
A Thorough Examination Of The Celebrated Performer's Life And Career Is Provided In Eduardo Yáñez.
Unveiling The Life Of Samira Khashoggi: A Journey Through Her Legacy.
A Complete Life Story And Career Summary Of Joyce Nettles.